Identify the Conditions for a Standard Electrochemical Cell.
Pressure of 1 atm Solution concentrations of 1 M Pressure of 5 atm Solute masses of 1 g Temperature of 273 K Temperature of 298 K Complete and balance the following redox reaction under acidic conditions. For a spontaneous reaction within an.
Solved Review Question 12 Status Not Yet Answered Points Chegg Com
2Fe 3 aq2e - underline 40 aq E 077 V Oxidation.

. 177 V 136 V - - 041 V For a spontaneous reaction within an electrochemical cell Ecell0. Solute masses of 1 g c. E cell -020 V 133 V.
E o cell E o reduction E o oxidation. Solution concentrations of 1M. Electrochemical cell 2 SCT Page 9 of 26 Q5.
Conditions for a standard electrochemical cell are - Pressure of 1 atm Solution concentrations of 1 M Temperature of 298 K Explanation- An el View the full answer. Has to be relative to another cell. Zns Cu 2 aq Zn 2 aq Cus Write the half-reactions for each process.
Identify the conditions for a standard electrochemical cell. G Identify the conditions for a standard electrochemical cell. Find the standard cell potential for an electrochemical cell with the following cell reaction and write its cell notation.
Temperature of 273 K d. The anode in these electrochemical cells is negatively charged whereas the cathode is positively charged. You can calculate the cell potential for an electrochemical cell from the half-reactions and the operating conditions.
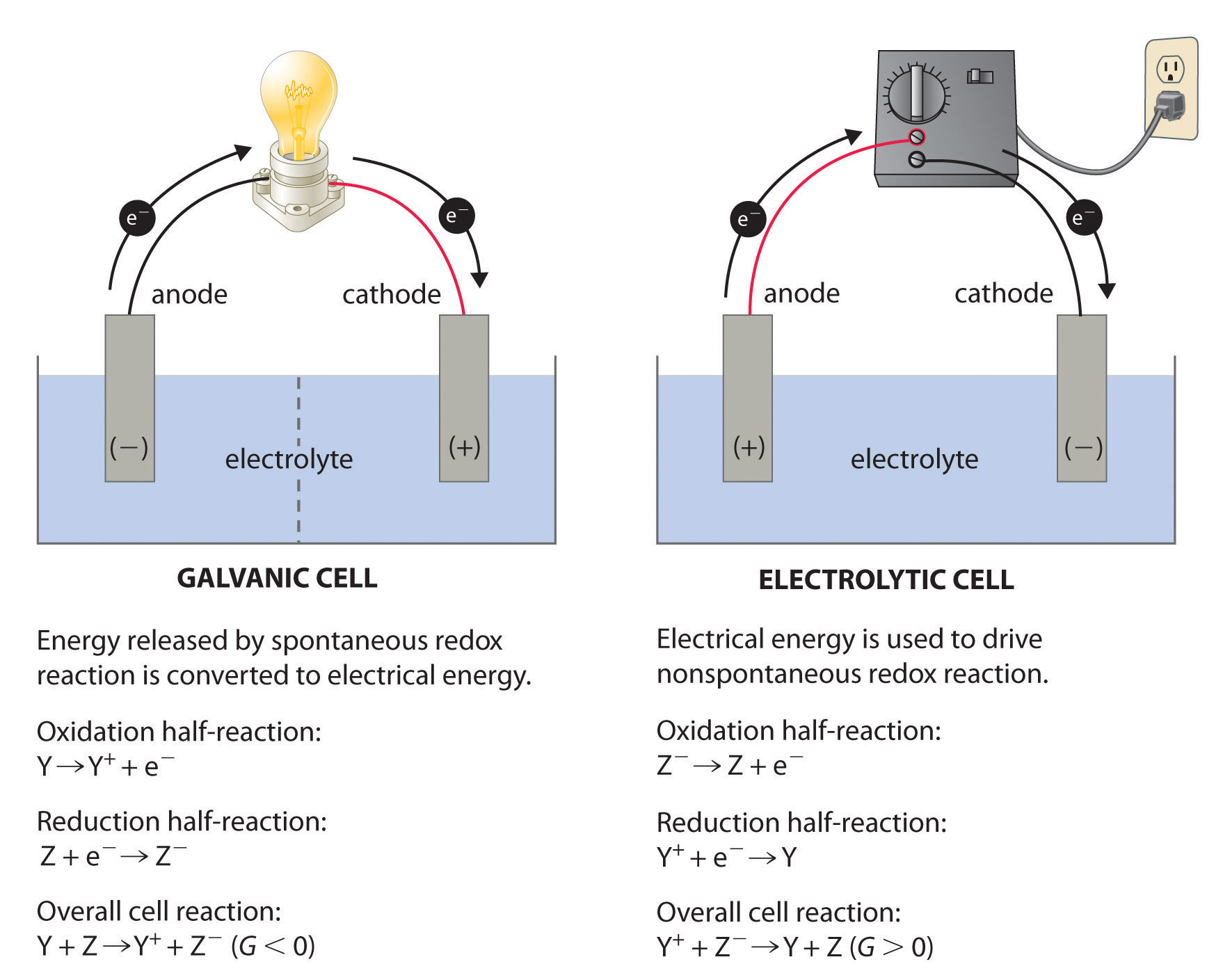
New questions in Chemistry Please help me solve this questions. But they arent the only kind of electrochemical cell. Add the potentials of the half-cells to get the overall standard cell potential.
BYJUS Online learning Programs For K3 K10 K12 NEET JEE UPSC Bank Exams. Temperature of 298 K d. Pressure of 1 atm b.
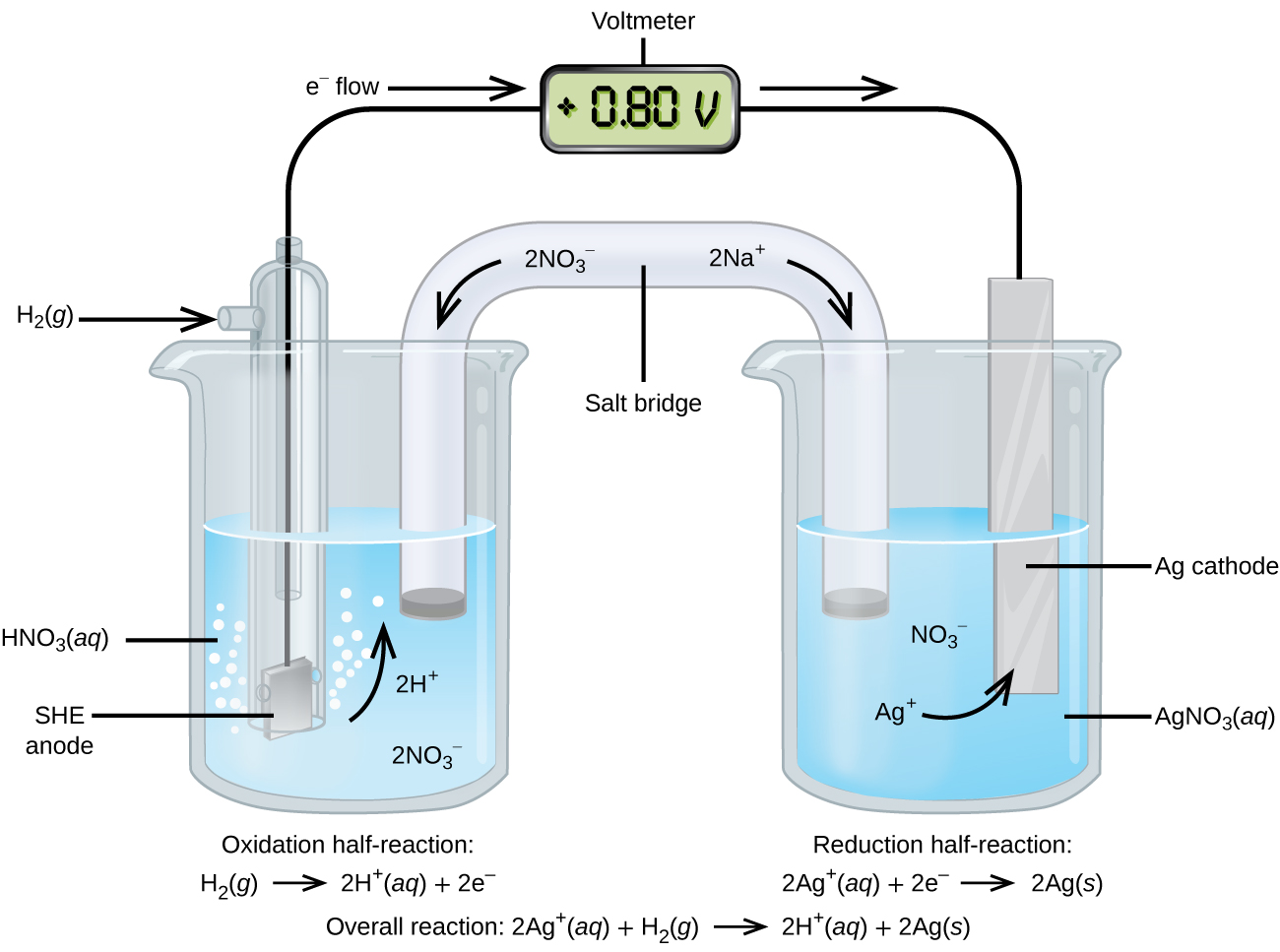
The standard condition for electro chemical cell measurements are Gases must be at 1 atm pressure. Solute masses of 1 g c. Standard Hydrogen Electrode SHE Consists of an inert platinum electrode in contact with 1 mol dm -3 hydrogen ions and hydrogen gas at 100 kPa and 298 K.
Hydrogenoxygen fuel cells can operate in acidic or in alkaline conditions but commercial cells use porous platinum electrodes in contact with concentrated aqueous potassium hydroxide. Pressure of 1 atm b. Voltaic cells use a spontaneous chemical reaction to drive an electric current through an external circuit.
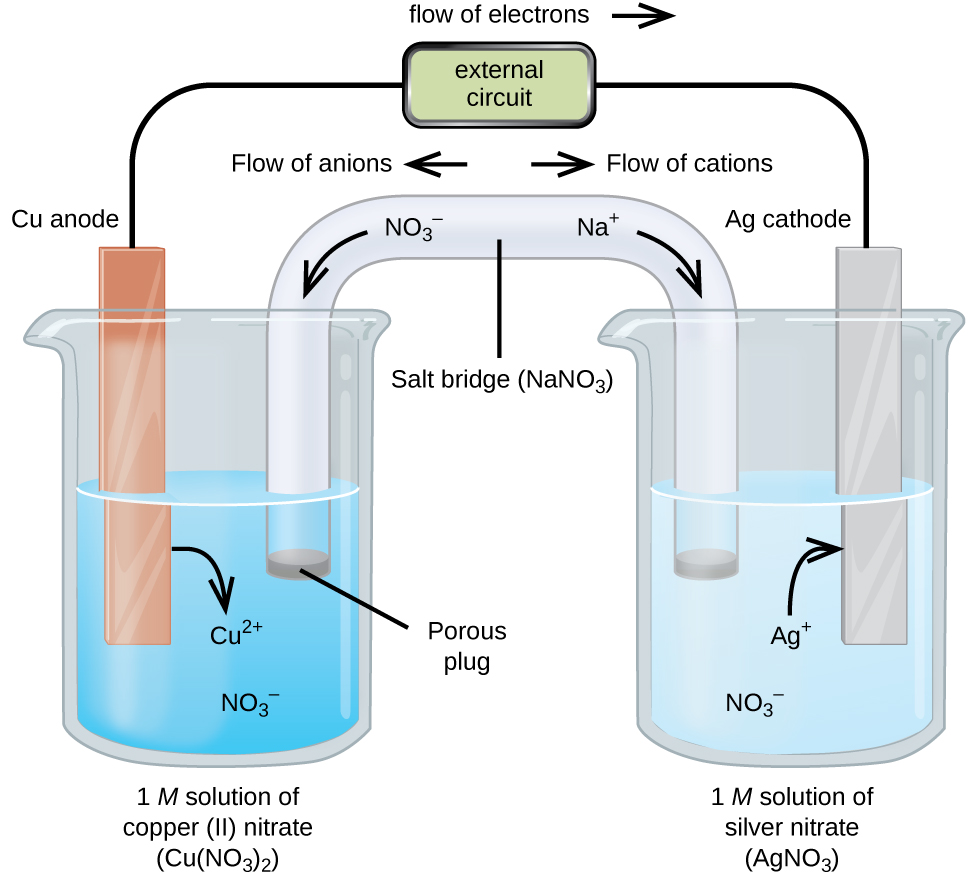
This electrochemical cell EMF example problem shows how to calculate cell potential of a cell from standard reduction potentials. Standard electrode potential of a single half-cell cannot be measured on its own. Zns Zn 2 aq 2 e-Cu 2 aq 2 e- Cus.
Solute masses Chemistry 12032022 1710 miathegeek97 Identify the conditions for a standard electrochemical cell. Temperature of 273 K d. For a non-spontaneous reaction within an electrochemical cell Ecell.
E cell E ox E red. This is an example of a gas electrode. The electrode potential EX for a half-cell X is defined as the potential measured for a cell comprised of X acting as cathode and the SHE acting as anode.
The table below shows some standard electrode potentials measured in acidic and in alkaline conditions. Temperature of 298 K d. Electrons come from somewhere else such as a battery.
Select one or more. Pressure of 1 atm b. Pressure of 1 atm Temperature of 298 K Solution concentrations of 1 M.
Which of the following is the correct expression to calculate the standard cell potential. Since the definition of cell potential requires the half-cells function as. Recall that oxidation takes place at the anode and reduction takes place at the cathode.
Pressure of 5 atm. If the electrolytes in the cells are not at standard conditions concentrations andor pressure they are included in parentheses with the phase notation. Pressure of 5 atm e.
Liquids must be in pure state Solids must also be in pure state Solutes are at 10 M concentration And the cell voltages are positive. Pressure of 5 atm e. Pressure of 1 atm b.
If no concentration or pressure is noted the electrolytes in the cells are assumed to be at standard conditions 100 M or 100 atm and 298 K. It is also possible to construct a cell that does work on a. The electrons are produced by the species that undergoes oxidation.
A positively charged anode and a negatively charged cathode are included in these cells. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel modern society. When the anode and cathode are connected by a wire electrons flow from anode to cathode.
Correct answer to the question Identify the conditions for a standard electrochemical cell. Pressure of 1 atm b. Calculate the cell potential.
Temperature Previous Next Chemistry 12032022 1710 miathegeek97 Identify the conditions for a standard electrochemical cell. Write the oxidation and reduction half-reactions for the cell. Identify the conditions for a standard electrochemical cell.
Find the standard cell potential for an electrochemical cell with the following cell reaction. Temperature of 273 K d. Temperature of 298 K d.
Select one or more. Solute masses of 1 g c. Cu s aq2e E.
The first step is to determine the cell potential at its standard state concentrations of 1 molL and pressures of 1 atm at 25C. Fe 3 aqe - underline 38 aq E 077 V 39 aq2 c Cu s E 034 V Solution. Solute masses of 1 g c.
A standard electrochemical cell is constructed from an anode that has a standard reduction potential of -20 V and a cathode that has a standard reduction potential of 05 V. When the half-cell X is under standard-state conditions its potential is the standard electrode potential EX. Identify the conditions for a standard electrochemical cell.
The reaction conditions pressure temperature concentration etc the anode the cathode and the electrode components are all described in this unique shorthand. Identify the conditions for a standard electrochemical cell. Fe 3 aqCu s Cu 2 aqFe 2 aq Given the following reduction potentials.
Solution concentrations of 1 M Solute masses of 1 g Temperature of 298 K Pressure of 1 atm Temperature of 273 K Pressure of 5 atm.
19 2 Describing Electrochemical Cells Chemistry Libretexts
0 Response to "Identify the Conditions for a Standard Electrochemical Cell."
Post a Comment